Our Services

design_services Satellite Design
We offer comprehensive satellite design services tailored to your mission requirements. From initial concept and feasibility studies to detailed engineering and systems integration, our team of experts ensures your pico-satellite is optimized for performance and reliability in orbit. Our modular architecture allows for rapid prototyping and customization, reducing development time and costs.

space_dashboard Orbital Mechanics
Mastering the dance of space. Our Orbital Mechanics service navigates your mission through the complexities of space, ensuring precision, efficiency, and reliability. From meticulous trajectory planning to precise orbital maneuvers and advanced simulations, we optimize every aspect of your satellite's journey.
Pico Satellite Launch Lifecycle
Follow our end-to-end process, from initial idea to post-mission analysis.
01 Conceptualization and Mission Definition
expand_more

click to enlarge
We work with you to define clear mission objectives, payload requirements, and conduct feasibility studies to ensure a solid foundation for your pico-satellite project. This phase establishes the scientific or commercial goals and outlines the mission architecture.
The journey begins with a clear understanding of the mission objectives. What problem are you trying to solve or what data are you trying to collect? For a pico satellite, which typically focuses on environmental monitoring, consider these aspects:
- Define the Mission: Clearly articulate the purpose of the satellite. Examples include measuring atmospheric pollutants, monitoring temperature variations, or detecting specific gases.
- Identify Key Parameters: Determine the specific environmental parameters to be measured. This will influence sensor selection and data processing requirements.
- Establish Success Criteria: Define measurable criteria to evaluate the mission's success. This could include the accuracy of data collected, the duration of operation, or the successful transmission of data to ground stations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Research and understand the regulatory requirements for launching a satellite, including obtaining necessary licenses and permits from relevant space agencies and international organizations.
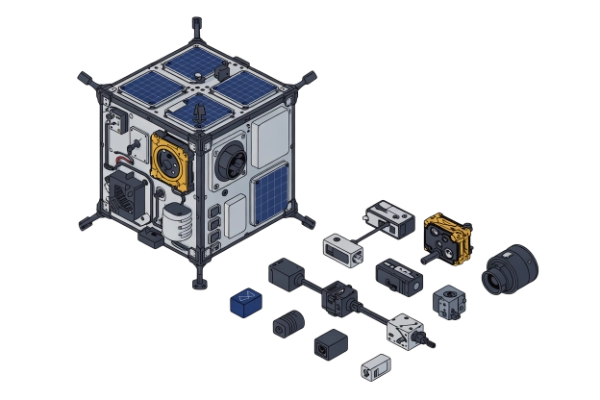
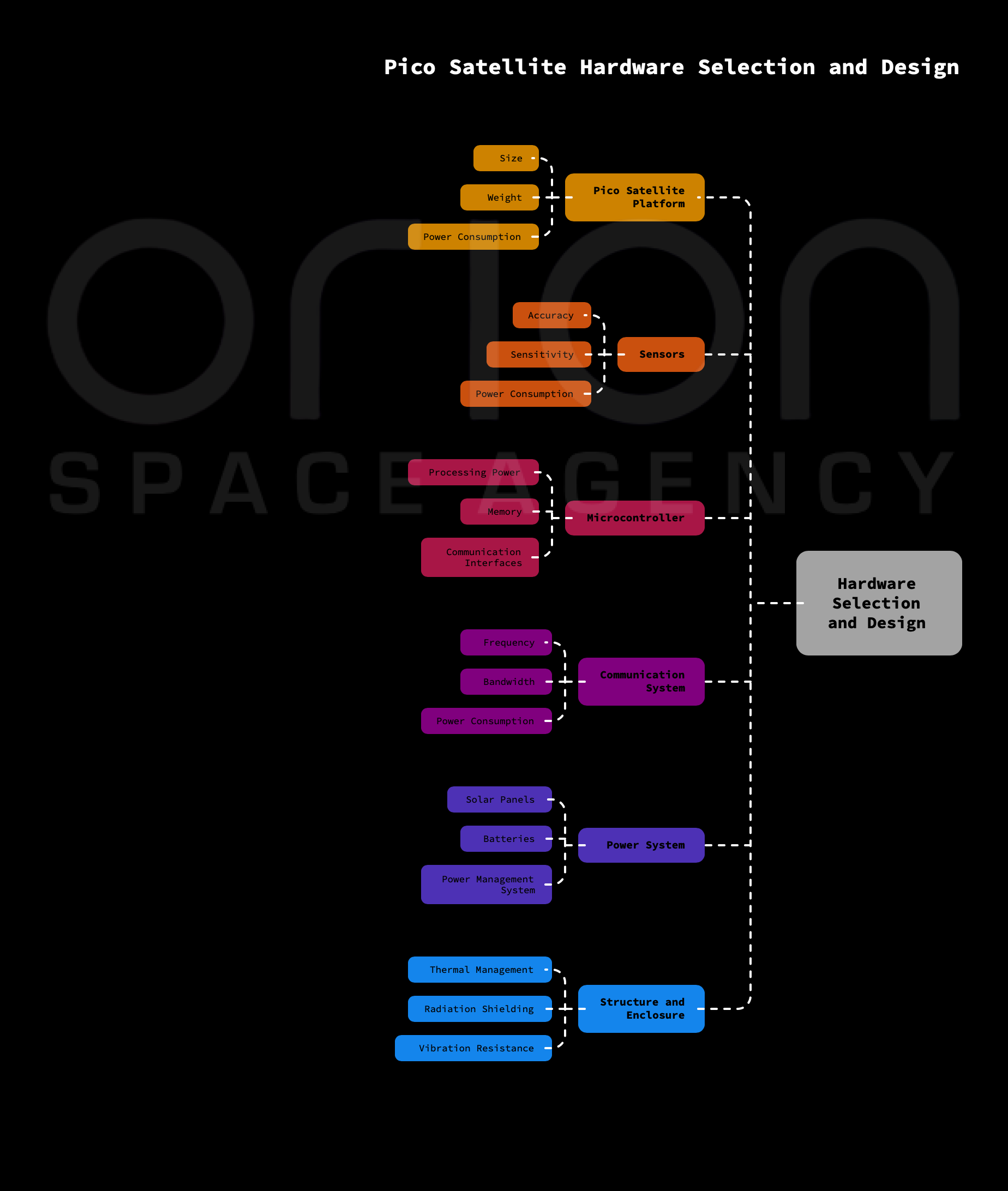
02 Hardware Selection and Design
expand_more
click to enlarge
Expert selection of COTS components and custom PCB design. We handle the mechanical engineering of the chassis and integration of power, communication, and payload subsystems to withstand the harsh space environment.
Choosing the right hardware components is crucial for the success of the mission. Consider the following:
- Pico Satellite Platform: Select a suitable satellite platform, considering its size, weight, power consumption, and available interfaces.
- Sensors: Choose sensors that are appropriate for measuring the desired environmental parameters. Consider factors such as accuracy, sensitivity, power consumption, and size.
- Microcontroller: Select a microcontroller with sufficient processing power, memory, and communication interfaces to handle data acquisition, processing, and transmission.
- Communication System: Choose a communication system that allows for reliable data transmission to ground stations. Consider factors such as frequency, bandwidth, power consumption, and antenna design.
- Power System: Design a power system that can provide sufficient power to all components throughout the mission. This typically involves solar panels, batteries, and a power management system.
- Structure and Enclosure: Design a robust structure and enclosure to protect the internal components from the harsh space environment. Consider factors such as thermal management, radiation shielding, and vibration resistance.
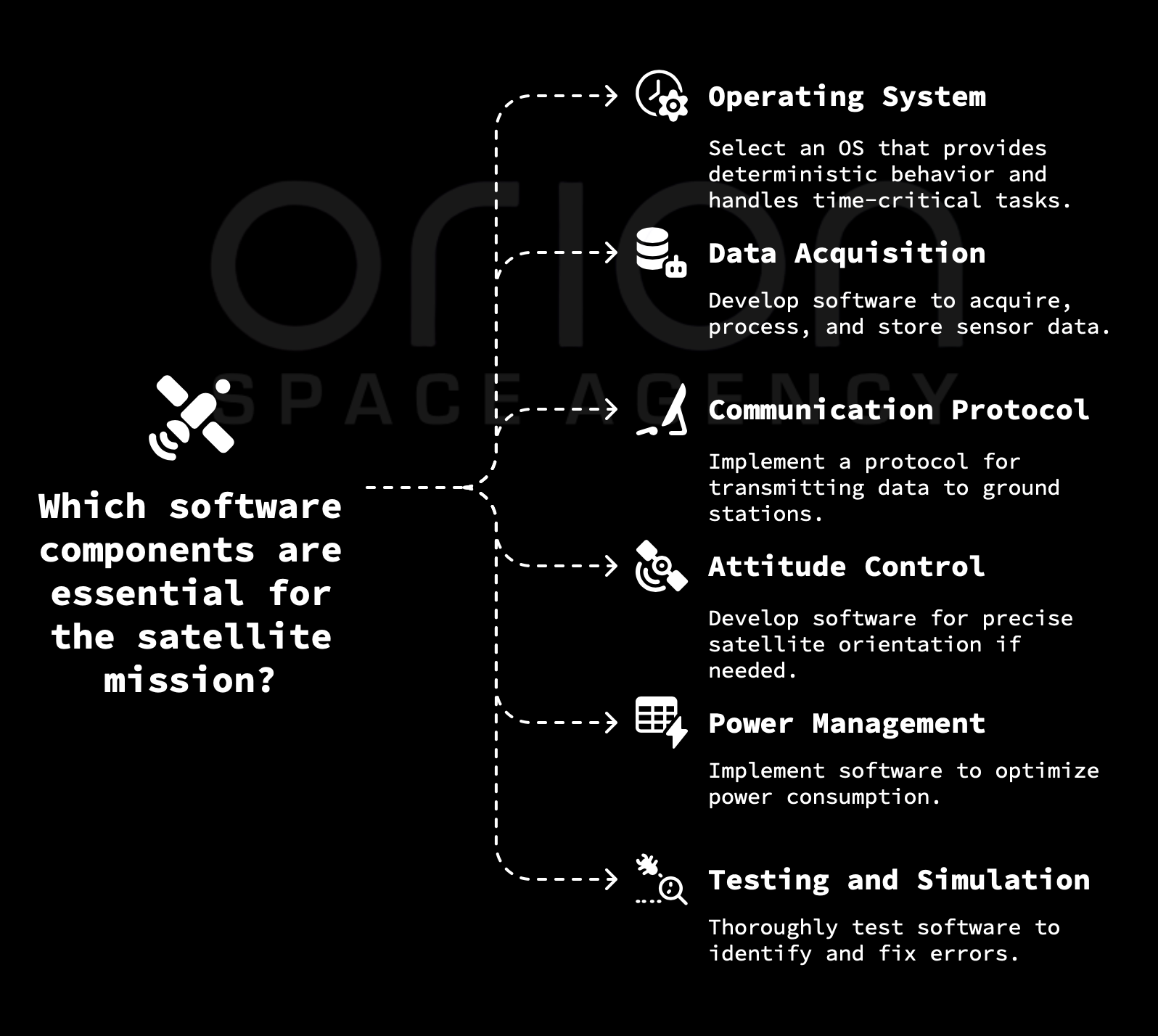
03 Software Development
expand_more
click to enlarge
Robust flight software development, including attitude determination and control systems (ADCS), payload management, and fault-tolerant communication protocols to ensure reliable operation in orbit.
Software is the brain of the satellite, controlling its operations and managing data.
- Operating System (OS): Choose a suitable OS for the microcontroller. Real-time operating systems (RTOS) are often preferred for their deterministic behavior and ability to handle time-critical tasks.
- Data Acquisition and Processing: Develop software to acquire data from the sensors, perform necessary calibration and filtering, and store the data in a suitable format.
- Communication Protocol: Implement a communication protocol for transmitting data to ground stations. This may involve encoding the data, adding error correction codes, and handling communication protocols.
- Attitude Control (If Applicable): If the mission requires precise attitude control, develop software to control the satellite's orientation.
- Power Management: Implement software to manage the power system, optimizing power consumption and ensuring that all components receive sufficient power.
- Testing and Simulation: Thoroughly test the software using simulations and hardware-in-the-loop testing to identify and fix any bugs or errors.
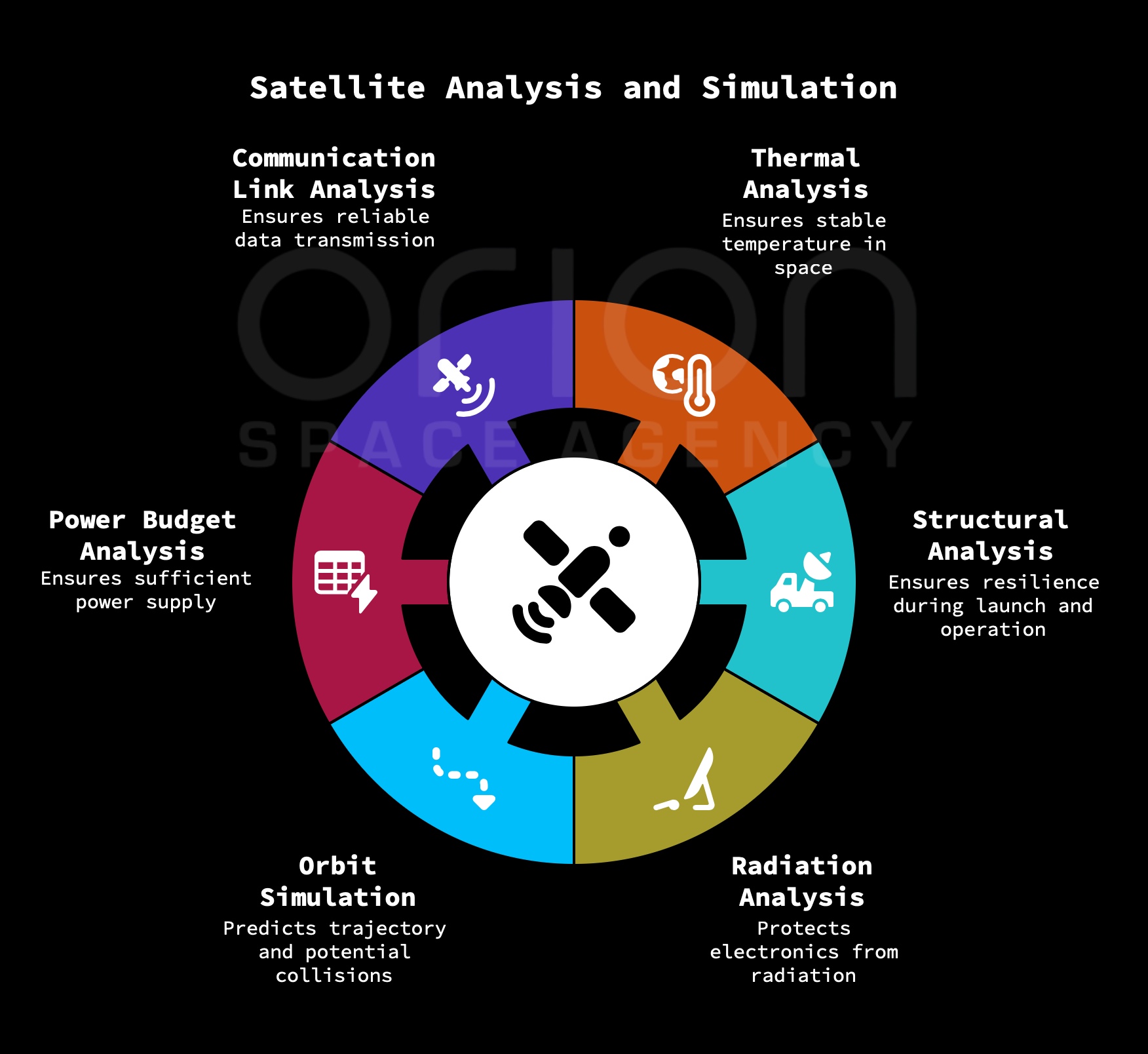
04 Analysis and Simulation
expand_more
click to enlarge
Comprehensive thermal, structural, and orbital simulations to validate design performance. We model extreme temperature cycles and launch loads to identify potential failure points before physical assembly.
Before launch, rigorous analysis and simulation are essential to ensure the satellite's survivability and performance.
- Thermal Analysis: Conduct thermal analysis to ensure that the satellite can maintain a stable temperature range in the harsh space environment.
- Structural Analysis: Perform structural analysis to ensure that the satellite can withstand the stresses and vibrations experienced during launch and operation.
- Radiation Analysis: Analyze the effects of radiation on the satellite's components and implement necessary shielding to protect sensitive electronics.
- Orbit Simulation: Simulate the satellite's orbit to predict its trajectory, visibility from ground stations, and potential collisions with other objects.
- Power Budget Analysis: Analyze the power consumption of all components to ensure that the power system can provide sufficient power throughout the mission.
- Communication Link Budget Analysis: Analyze the communication link between the satellite and ground stations to ensure that data can be transmitted reliably.
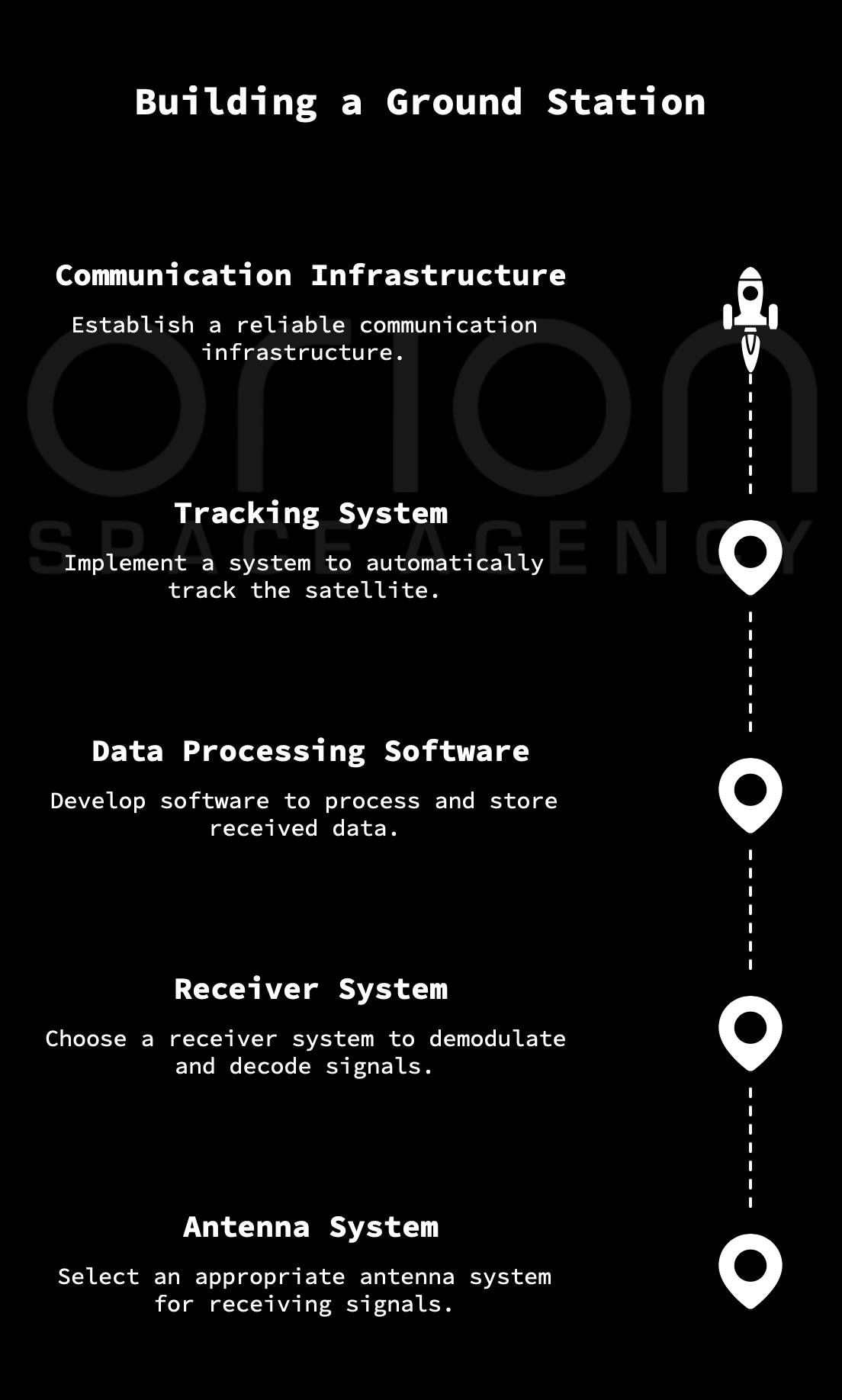
05 Ground Station Development
expand_more
click to enlarge
Setup and configuration of ground station infrastructure for reliable uplink/downlink communication. We ensure your mission control center is ready for tracking and data acquisition.
A ground station is essential for communicating with the satellite and receiving data.
- Antenna System: Select an appropriate antenna system for receiving signals from the satellite. Consider factors such as gain, bandwidth, and tracking capabilities.
- Receiver System: Choose a receiver system that can demodulate and decode the signals from the satellite.
- Data Processing Software: Develop software to process the received data, extract relevant information, and store it in a database.
- Tracking System: Implement a tracking system to automatically track the satellite as it orbits the Earth.
- Communication Infrastructure: Establish a reliable communication infrastructure for transmitting data from the ground station to a central data processing center.
06 Launch Preparation
expand_more

click to enlarge
Final assembly, integration, and rigorous testing (vibration, thermal vacuum). We also assist with licensing, frequency allocation, and regulatory compliance to clear your satellite for flight.
Preparing the satellite for launch involves a series of critical steps.
- Final Assembly and Testing: Perform a final assembly of all components and conduct comprehensive testing to ensure that everything is working correctly.
- Environmental Testing: Subject the satellite to environmental testing, including vibration testing, thermal vacuum testing, and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing, to simulate the conditions it will experience during launch and operation.
- Integration with Launch Vehicle: Integrate the satellite with the launch vehicle, following the procedures and requirements specified by the launch provider.
- Pre-Launch Checks: Conduct pre-launch checks to ensure that all systems are functioning correctly and that the satellite is ready for launch.
- Transportation to Launch Site: Transport the satellite to the launch site, following strict procedures to ensure its safety and security.
07 Launch and Deployment
expand_more

click to enlarge
Coordination with launch providers, integration into the deployer, and monitoring of the launch sequence. We oversee the critical moment of orbital insertion and initial beacon acquisition.
The launch is the culmination of all the hard work and preparation.
- Launch Monitoring: Monitor the launch process closely, tracking the satellite's trajectory and performance.
- Deployment: Verify that the satellite has been successfully deployed from the launch vehicle.
- Initial Contact: Attempt to establish initial contact with the satellite and verify that its systems are functioning correctly.
- Orbit Determination: Determine the satellite's precise orbit using tracking data from ground stations.
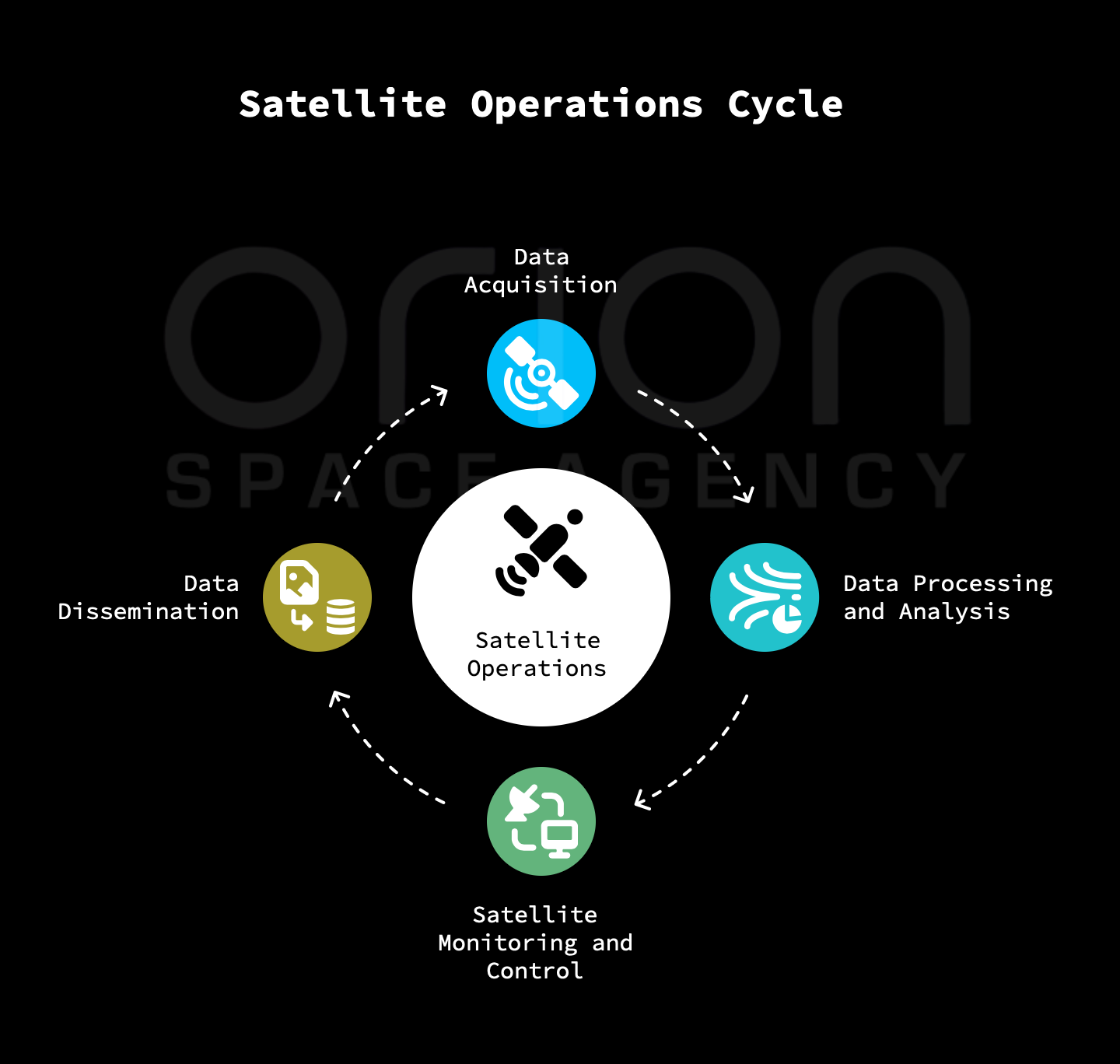
08 Operations and Data Analysis
expand_more
click to enlarge
Ongoing mission operations, satellite health monitoring, and processing of scientific data. We turn raw telemetry into actionable insights and manage daily command cycles.
Once the satellite is in orbit, the focus shifts to operations and data analysis.
- Data Acquisition: Collect data from the satellite on a regular basis, using the ground station network.
- Data Processing and Analysis: Process and analyze the collected data to extract meaningful information and validate the mission objectives.
- Satellite Monitoring and Control: Monitor the satellite's health and performance, and issue commands to adjust its operations as needed.
- Data Dissemination: Disseminate the collected data to researchers, policymakers, and the public.
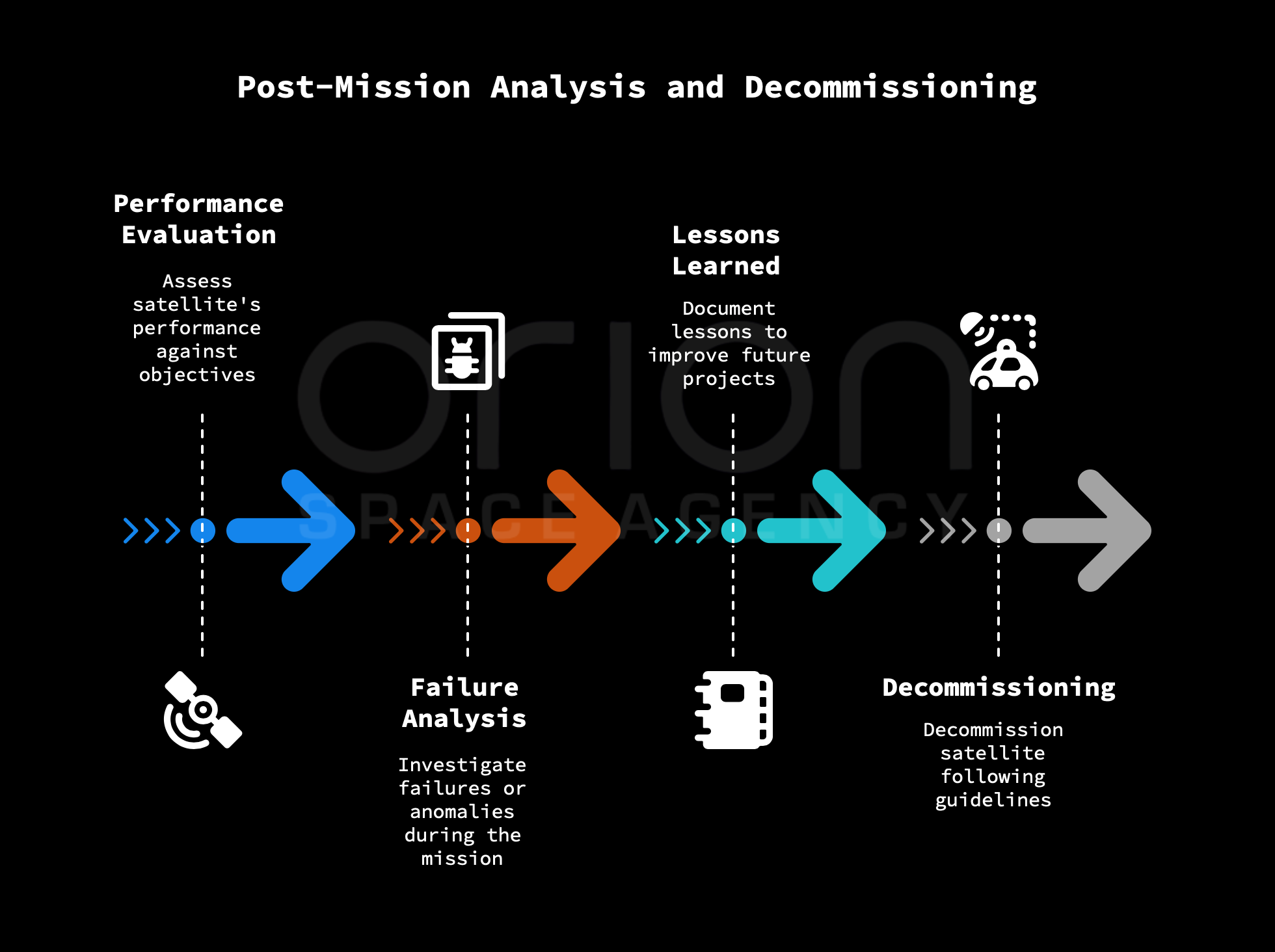
09 Post-Mission Analysis
expand_more
click to enlarge
Comprehensive review of mission performance, data archiving, and planning for safe deorbiting and disposal. We ensure compliance with space debris guidelines and document lessons learned.
After the mission is complete, conduct a post-mission analysis to evaluate its success and identify lessons learned.
- Performance Evaluation: Evaluate the satellite's performance against the original mission objectives.
- Failure Analysis: Investigate any failures or anomalies that occurred during the mission.
- Lessons Learned: Document the lessons learned from the mission to improve future satellite projects.
- Decommissioning: Decommission the satellite in a responsible manner, following international guidelines for space debris mitigation.
